3D printing in dentistry is a manufacturing tool that creates the products needed for each patient's needs and shape
Read more: One of the areas where 3D printing is becoming increasingly popular is dentistry. 3D printing in dentistry is a manufacturing tool that allows for the creation of desired products based on each patient's needs and form. Whether through the use of resin additive manufacturing or powder bed fusion additive manufacturing, it can open new doors for professionals in dental offices and laboratories. In addition, dental 3D printing often goes hand in hand with other digital solutions, such as new CAD tools for capturing the anatomy of a patient's teeth or dental 3D scanners. In short, this new technology offers a wide range of benefits for dentistry. Below, Mohou.com describes the main applications of 3D printing in dentistry.

● 3D scanning in dentistry
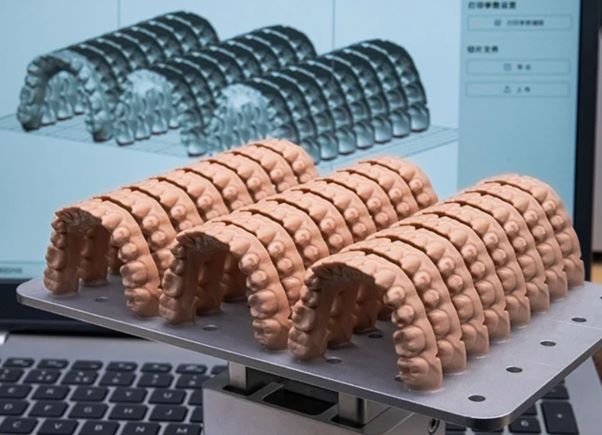
Although this is not a dental 3D printing application per se, we cannot fail to mention 3D scanning. The use of 3D scanners is becoming more and more common when it comes to 3D printed dentistry. This is the first step in the digital workflow, and with the help of 3D scanners, medical professionals are able to digitize the inside of a patient's mouth using an intraoral scanner, or digitize an impression with a laboratory scanner. A digital file of the impression is created and can be exported in STL format for 3D printing. One of the advantages of using a 3D dental scanner is the high accuracy. It also offers the possibility to produce customized devices depending on the patient's dental morphology. For example, if a patient needs an emergency prosthesis, there is no need to leave new model data, as these models have already been digitized in previous treatments, saving the patient and the healthcare provider a lot of time.

△ Dental 3D Scanner Image Source: 3Shape
●Dental crowns and bridges
Crowns and bridges are the most common products used in dental treatment methods, as they can be used to replace missing teeth. The essential difference between the two is that crowns are used to cover damaged or decayed teeth and can be placed on top of the damaged area. They can also cover dental implants in the absence of teeth. Bridges are used to replace missing teeth and consist of two crowns (one at each end) and certain prosthetic bridges. 3D printing is becoming more and more widespread in the field of dentistry, allowing the use of resin 3D printing to create temporary, highly accurate and aesthetically pleasing 3D printed crowns and bridges. The technology is becoming increasingly popular because it is more cost effective and faster to produce than traditional milling processes.
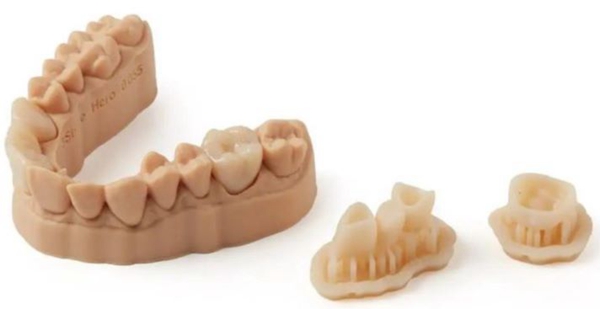
△ Markforged image credit: Formlabs
● Aligners and Retainers
Additive manufacturing is producing more and more dental devices, which not only increases the speed of manufacturing but also enables personalization, a very important aspect of the field, as every person's teeth are different. Retainers, or braces, are devices that are used to move a patient's teeth. First the healthcare provider scans the patient's mouth and then, using CAD software, obtains the required files and exports them to the 3D printer that will be used for printing. The most commonly used technology is resin 3D printing, such as SLA, DLP or MSLA. depending on the user's needs, some parameters can be changed, such as print time, print area, etc.
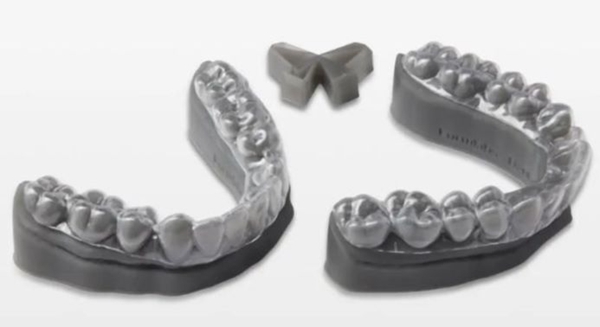
△ Image source: Formlabs
●Implants
Whenever we lose a tooth, we need a quick treatment with implants, otherwise the missing area around the tooth will degrade due to lack of pressure. With the help of additive manufacturing, implants in dentistry can not only be produced on demand and therefore faster, but also personalized. This is especially important in dental care, as each person's mouth and smile are unique to them. With 3D printed precision manufacturing methods used for dental implant surgery, patients are not limited in their ability to bite or chew in any way. In addition, 3D printing is also considered to be a more economical method that is constantly improving through innovation, making the production of dental implants much easier.
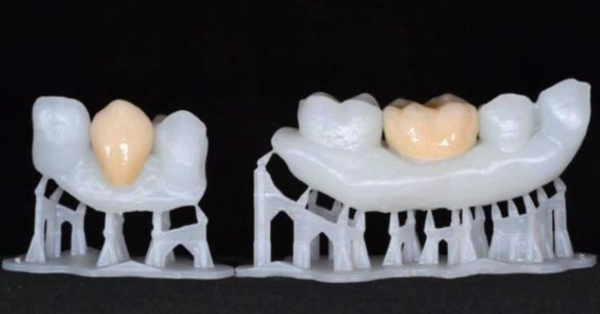
△ Image source: Formlabs
● Surgical guides
One use of 3D printing that is particularly valuable to dentistry is surgical guides for dental implants. This is one of the latest advances that has revolutionized surgical procedures even outside of dentistry. During surgery, it is sometimes difficult for dentists to place implants in the correct position due to inconvenient angles and the inability to see clearly. As a result, many implants are placed in the wrong place, which can lead to many oral health complications. The surgical guide is designed to solve these problems. Specifically, the guide helps the dentist to place the dental implant in the correct position. It is a disposable device that can be placed directly on the patient's teeth and has a hole that allows the implant to be placed in the correct position at the correct angle and depth. This method offers a higher degree of precision, approximately three times better than manual placement.
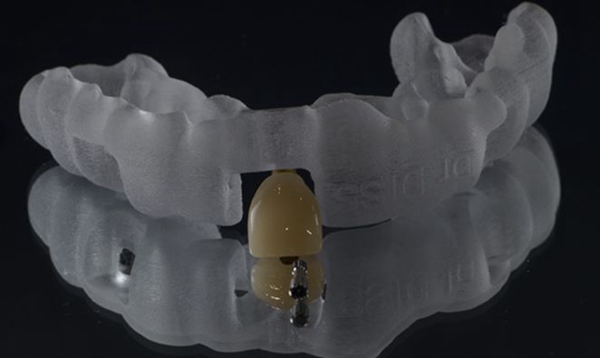
△ Photo credit: Arias Dentistry
● Anatomical replicas and models
For dentistry, an anatomical model is the jaw or mouth. Models are used in planning and discussing surgical procedures between patient-clinician and clinician-clinician. They provide a detailed image of the desired area and can reduce the risk of operative error because the dentist has a physical anatomical structure to work with. what does 3D printing do in this specifically? Traditionally making plaster models of crowns and dentures is a slow manual process and requires waiting for the model to be ready. 3D printing can be used to generate models based on intraoral scans in a fast and efficient way, as it is built layer by layer by the printer. For basic models, FDM with filaments can be used, but for more complex replicas, resin models can be produced with SLA.

△ Oral anatomy model Image source: freepik.com
● Dentures
The use of 3D printing to produce dentures is an emerging technology that has the advantage of simplifying the process. The traditional method of making dentures is milling through a resin base, which is complex and time-consuming and requires multiple visits to the dentist. 3D printing can produce dentures in a faster and cheaper way. Although the method is not perfect at the moment, limited by aesthetics and low-resolution printers, there have been many developments. Recently, new materials used to produce dentures have received CE markings (i.e., marked as safe in the EEA) and patient studies have shown that dentures are acceptable to users. some companies such as Formlabs already offer custom denture solutions, and their website suggests savings of more than half the cost compared to fully milled teeth.

△ 3D printed denture set (left) and a milled set (right). Photo credit: Aegis Dental Network
● Casting models
3D printing can also be used for indirect dental procedures. Often 3D printing can be used to make dental end-use parts, including crowns and bridges, inner crowns and substructures, but it also plays a role in making castings. Dental casting models are accurate three-dimensional replicas of a patient's teeth that can be used not only to study the mouth, but also to create crowns, fixed bridges and dentures. Anyone who has done orthodontic work or seen a dentist has had the experience of biting down on uncomfortable wax to make such molds. With 3D scanning and printing, the process is simplified by printing, cleaning, removing supports, and sintering to create a high-precision mold that results in a final product.















